Sewage and Sewage Analysis Sewage treatment is the process of removing most of the pollutants from wastewater or sewage and producing a liquid effluent suitable for disposal into the natural environment and sludge. To be effective, sewage must be transported to treatment plants by proper piping and infrastructure, and the process itself must be regulated and controlled. Other wastewaters often require different and sometimes specialized treatment methods. In the simplest sewage treatment and most wastewater treatments, the solids are usually separated from the liquid by settling. Produces an effluent stream of increasing purity by gradually converting dissolved material to solids, usually biota, and settling them out.
Describe
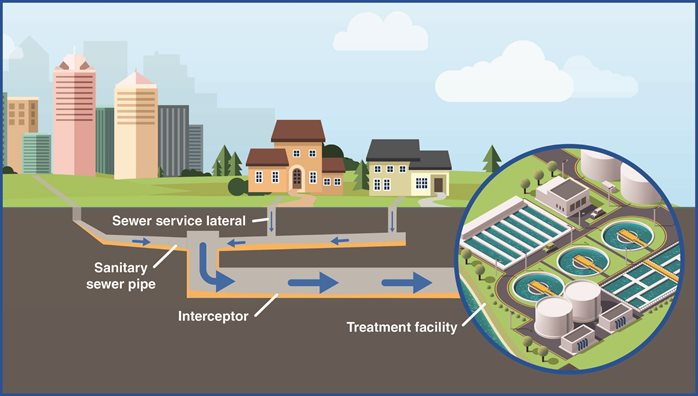
Sewage is liquid waste from toilets, bathrooms, showers, kitchens, etc. that is disposed of through the sewer. In many areas, sewage also includes some liquid waste from industry and commerce. In many countries, waste from toilets is called foul waste, waste from items such as basins, bathrooms and kitchens is called sludge water, and industrial and commercial waste is called trade waste. It is becoming more common in developed countries to divide household water into gray and black water, with gray water being allowed to water plants or recycled for flushing toilets. Many sewages also include some surface water from roofs or hard areas. Thus, municipal wastewater includes residential, commercial, and industrial liquid discharges and may also include stormwater runoff.
General test parameters:
·BOD (biochemical oxygen demand)
·COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand)
·MLSS (Mixed Liquid Suspended Solids)
·Oil and grease
·PH
·Conductivity
·Total dissolved solids
BOD (biochemical oxygen demand):
Biochemical Oxygen Demand, or BOD, is the amount of dissolved oxygen required by aerobic organisms in a body of water to decompose the organic matter present in a given water sample at a specific temperature for a specific time period. The term also refers to the chemical procedures used to determine the amount. This is not an exact quantitative test, although it is widely used as an indicator of the organic quality of water. BOD can be used as an indicator to measure the efficiency of wastewater treatment plants. It is listed as a routine pollutant in most countries.
COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand):
In environmental chemistry, the chemical oxygen demand (COD) test is often used to indirectly measure the amount of organic compounds in water. Most applications of COD determine the amount of organic pollutants found in surface water (such as lakes and rivers) or wastewater, making COD a useful indicator of water quality. Many governments have imposed strict regulations on the maximum chemical oxygen demand allowed in wastewater before it is returned to the environment.
Our company enters water treatment industry since 1985 by providing the chemicals and solutions for all kinds of industrial and municipal sewage treatment plants. We are the manufacturer of water treatment chemicals, including Polyethylene glycol-PEG, Thickener,Cyanuric Acid, Chitosan, Water Decoloring Agent, Poly DADMAC, Polyacrylamide, PAC, ACH, Defoamer, Bacteria Agent, DCDA, etc.
If you are interested, pls contact us for free samples.
Post time: Nov-21-2022

